Spironolactone CAS NO 52-01-7 Inquire about Spironolactone
Tecoland supplies Spironolactone bulk active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) to the pharmaceutical industry. Our Spironolactone is manufactured by cGMP compliant facility. Welcome to contact us for further details including current DMF status for the product and up to date regulatory status of the manufacturing facility. We look forward to assisting you with your research and development projects.
What is Spironolactone?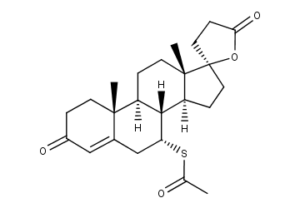
Spironolactone (INN, BAN, USAN), commonly referred to simply as “spiro”, and marketed primarily under the brand name Aldactone in most countries, is a synthetic, steroidal antimineralocorticoid agent with additional antiandrogen and weak progestogen properties, as well as some indirect estrogen and glucocorticoid effects, which is used primarily as a diuretic and antihypertensive, but also for the purpose of reducing elevated or unwanted androgen activity in the body. It acts predominantly as a competitive antagonist of the aldosterone (or mineralocorticoid) receptor, and belongs to a class of pharmaceutical drugs known as potassium-sparing diuretics.
Spironolactone is a relatively old drug, having been introduced clinically in 1959. It has been predicted that spironolactone will be superseded in cardiovascular conditions (e.g., heart failure and hypertension) by the newer agents such as the structurally related compound eplerenone, which is also an aldosterone antagonist but is selective and lacks many of the actions and side effects of spironolactone, and as such is much more tolerable in comparison. However, spironolactone is still far more widely used than eplerenone. Spironolactone nonetheless still finds frequent use as an antiandrogen.
Pharmacodynamics
Spironolactone is a synthetic 17-lactone steroid which is a renal competitive aldosterone antagonist in a class of pharmaceuticals called potassium-sparing diuretics. On its own, spironolactone is only a weak diuretic, but it can be combined with other diuretics. Due to its anti-androgen effect, it can also be used to treat hirsutism, and is a common component in hormone therapy for male-to-female transgendered people. Spironolactone inhibits the effect of aldosterone by competing for intracellular aldosterone receptor in the distal tubule cells. This increases the secretion of water and sodium, while decreasing the excretion of potassium. Spironolactone has a fairly slow onset of action, taking several days to develop and similarly the effect diminishes slowly.
What is the mechanism of action?
Spironolactone is a specific pharmacologic antagonist of aldosterone, acting primarily through competitive binding of receptors at the aldosterone-dependent sodium-potassium exchange site in the distal convoluted renal tubule. Spironolactone causes increased amounts of sodium and water to be excreted, while potassium is retained. Spironolactone acts both as a diuretic and as an antihypertensive drug by this mechanism. It may be given alone or with other diuretic agents which act more proximally in the renal tubule. Aldosterone interacts with a cytoplasmic mineralocorticoid receptor to enhance the expression of the Na+, K+-ATPase and the Na+ channel involved in a Na+ K+ transport in the distal tubule. Spironolactone binds to this mineralcorticoid receptor, blocking the actions of aldosterone on gene expression. Aldosterone is a hormone; its primary function is to retain sodium and excrete potassium in the kidneys.
How should Spironolactone be used?
Spironolactone comes as a tablet to take by mouth. It usually is taken once a day in the morning or sometimes twice a day. Take spironolactone at around the same time(s) every day. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully. Take spironolactone exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Your doctor may start you on a low dose of spironolactone and gradually increase your dose.
What are the side effects of Spironolactone?
The most common side effect of spironolactone is urinary frequency. Other general side effects include ataxia, drowsiness, dry skin, and rashes. Because it also affects the androgen receptors, spironolactone can cause gynecomastia and feminization in general, testicular atrophy, and sexual dysfunction consisting of loss of libido and erectile dysfunction, and in females it can cause menstrual irregularities and breast tenderness and enlargement.
Spironolactone may put patients at a heightened risk for bleeding from the stomach and duodenum, though a causal relationship between the two has not been established. Also, it has been shown to be immunosuppressive in the treatment of sarcoidosis.
Toxicology
The oral LD50 of spironolactone is greater than 1,000 mg/kg in mice, rats, and rabbits. Acute overdosage of spironolactone may be manifested by drowsiness, mental confusion, maculopapular or erythematous rash, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, or diarrhea. Spironolactone has been shown to be a tumorigen in chronic toxicity studies in rats.
Storage
Keep spironolactone in the container it came in, tightly closed, and out of reach of children. Store it at room temperature and away from excess heat and moisture (not in the bathroom).
Disclaimer:
Information on this page is provided for general information purposes. You should not make a clinical treatment decision based on information contained in this page without consulting other references including the package insert of the drug, textbooks and where relevant, expert opinion. We cannot be held responsible for any errors you make in administering drugs mentioned on this page, nor for use of any erroneous information contained on this page.