Thiamphenicol CAS NO 15318-45-3 Inquire about Thiamphenicol
Tecoland supplies Thiamphenicol bulk active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) to the pharmaceutical industry. Our Thiamphenicol is manufactured by cGMP compliant facility. Welcome to contact us for further details including current DMF status for the product and up to date regulatory status of the manufacturing facility. We look forward to assisting you with your research and development projects.
What is Thiamphenicol?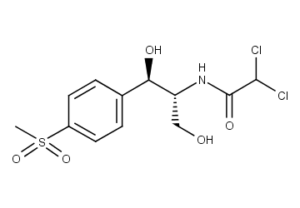
Thiamphenicol (also known as thiophenicol and dextrosulphenidol) is an antibiotic.[1] It is the methyl-sulfonyl analogue of chloramphenicol and has a similar spectrum of activity, but is 2.5 to 5 times as potent. Like chloramphenicol, it is insoluble in water, but highly soluble in lipids. It is used in many countries as a veterinary antibiotic, but is available in China, Morocco and Italy for use in humans. Its main advantage over chloramphenicol is that it has never been associated with aplastic anaemia.
Thiamphenicol is also widely used in Brazil, particularly for the treatment of sexually transmitted infections and pelvic inflammatory disease.[2]
Unlike chloramphenicol, thiamphenicol is not readily metabolized in cattle, poultry, sheep, or humans, but is predominantly excreted unchanged. In pigs and rats the drug is excreted both as parent drug and as thiamphenicol glucuronate (FAO, 1997).
Chemical Formula
C12-H15-Cl2-N-O5-S
Molecular Weight
356
Therapeutic Category
Antibacterial: Chloramphenicol
Chemical Name
Acetamide, 2,2-dichloro-N-[2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymetyl)-2-[4-(metylsulfonyl)phenyl]etyl]-, [R-(R*,R*)]-
Foreign Names
- Thiamphenicolum (Latin)
- Thiamphenicol (German)
- Thiamphénicol (French)
- Tiamfenicol (Spanish)
Generic Names
- Thiamphenicol (OS: USAN, JAN, BAN)
- Thiamphénicol (OS: DCF)
- Tiamfenicolo (OS: DCIT)
- Dextrosulfenidol (IS)
- Vicemycetin (IS)
- Win 5063-2 (IS)
- Thiamphenicol (PH: BP 2018, Ph. Eur. 9)
- Thiamphénicol (PH: Ph. Eur. 9)
- Thiamphenicolum (PH: Ph. Eur. 9)
- Tiamfenicolo (PH: Ph. Eur. 9)
- Tiamfenicolo glicinato cloridrato (PH: F.U. XII)
General
Thiamphenicol is an antimicrobial substance intended for the treatment of infectious diseases in cattle, pigs and poultry. It is used as the water soluble thiamphenicol glycine hydrochloride for parenteral therapy and as a premix composed of thiamphenicol base and corn starch, (4:1) or other mixer, for oral use.
Thiamphenicol has a similar antibacterial spectrum to chloramphenicol (Van Beers et al 1975, Sutter and Finegold, 1976). It has not been associated with aplastic anaemia in spite of extensive use in man (Yunis et al 1973).
Thiamphenicol inhibits protein synthesis in bacteria. It has a bacteriostatic action against a broad range of microorganisms, although it may be bactericidal for some species under some conditions, and in concentrations 3 to 5 times higher than the bacteriostatic concentrations (Martindale 1971, 1973). Among the bacteria inhibited in vitro by relatively low concentrations of thiamphenicol are Clostridium, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Diplococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus albus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus viridans, Bacteroides, Fusobacterium, Bordatella, Brucella, Haemophilus, Neisseria, Pasteurella, Shigella and some vibrio strains. Some Bacilli, Erysipelothrix, Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus faecalis are sensitive to moderate concentrations of thiamphenicol but Listeria, Aerobacter, Escherichia, Klebsiella, Proteus and Salmonellae are sensitive only to relatively high concentrations. The compound is active against Mycoplasmas, Treponema, Rickettsias, Entamoeba and Actinomycetes, but inactive against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Ravizzola et al 1984). The in vitro antimicrobial activity of the thiamphenicol glycinate ester is similar to that of thiamphenicol base.
MIC studies using standard dilution methods were carried out by the sponsor in 1989 and show MIC50-values which are broadly similar to those described above, and by O’Grady et al (1980), but a few strains of Bacteroides, Escherichia coli, Salmonellae, Staphylococci, and Pasteurellae show high MICs in vitro.
As a summary thiamphenicol is a broad-spectrum antibiotic, active against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and especially effective against anaerobes. Thiamphenicol may be used in the treatment and control of a wide range of respiratory and alimentary tract infections of bacterial origin in calves, pigs and poultry. The oral product is not suitable for the treatment of cattle with functional rumen.
Dosage
There appears to be no firm recommendation of dosages in the dossier. Both 30 and 60 mg/kg have been used for calves, 20 – 40 mg/kg for pigs, 15 to 67 mg/kg for poultry, and 30 mg/kg in dairy cows. The oral preparations are not for use in ruminating animals. Administration for sucking calves includes 30 mg/kg of body weight daily of active ingredient, rate of addition to feed being 1000-1500 g/100 kg of milk powder, for pigs 20-30 mg/kg of body weight daily of active ingredient, rate of addition to feed 300-450 g/100 kg and for poultry, rate of addition to feed 400 g/100 kg and to water 200 g/100
Disclaimer:
Information on this page is provided for general information purposes. You should not make a clinical treatment decision based on information contained in this page without consulting other references including the package insert of the drug, textbooks and where relevant, expert opinion. We cannot be held responsible for any errors you make in administering drugs mentioned on this page, nor for use of any erroneous information contained on this page.
External Link:
- Wikipedia contributors. (2021, January 22). Thiamphenicol. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 19:33, February 2, 2021, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Thiamphenicol&oldid=1001997174
- Thiamphenicol. (n.d.). Drugs.Com. https://www.drugs.com/international/thiamphenicol.html
- Thiamphenicol. (n.d.-b). Fao.Org. http://www.fao.org/3/w4601e0d.htm