Azacitidine CAS NO 320-67-2 Inquire about Azacitidine
Tecoland supplies Azacitidine bulk active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) to the pharmaceutical industry. Our Azacitidine is manufactured by cGMP compliant facility. Welcome to contact us for further details including current DMF status for the product and up to date regulatory status of the manufacturing facility. We look forward to assisting you with your research and development projects.
What is Azacitidine?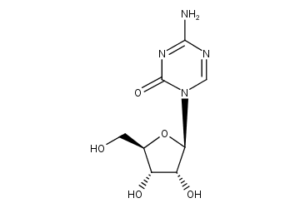
Azacitidine is a chemical analogue of cytidine, a nucleoside present in DNA and RNA. Azacitidine and its deoxy derivative, decitabine (also known as 5-aza-2?deoxycytidine), are used in the treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome. Both drugs were first synthesized in Czechoslovakia as potential chemotherapeutic agents for cancer.
Azacitidine is mainly used in the treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), for which it received approval by the U.S.Food and Drug Administration on May 19, 2004; it is marketed as Vidaza. In a randomized controlled trial comparing azacitidine to supportive treatment of MDS, around 16% of people receiving the drug had a complete or partial response—blood cell counts and bone marrow morphology returning to normal—and 2/3 patients who required blood transfusions before the study no longer needed them after receiving azacitidine.
It can also be used in vitro to remove methyl groups from DNA. This may weaken the effects of gene silencing mechanisms that occurred prior to the methylation. Methylation events are therefore believed to secure the DNA in a silenced state. Demethylation may reduce the stability of silencing signals and thus confer relative gene activation.
Azacitidine induces tumor regression on IDH1 mutant glioma xenografts in mice.
Mechanism of Action
Azacitidine is a chemical analogue of the cytosine nucleoside used in DNA and RNA. Azacitidine is thought to induce antineoplastic activity via two mechanisms; inhibition of DNA methyltransferase at low doses, causing hypomethylation of DNA, and direct cytotoxicity in abnormal hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow through its incorporation into DNA and RNA at high doses, resulting in cell death. As azacitidine is a ribonucleoside, it incorporates into RNA to a larger extent than into DNA. The incorporation into RNA leads to the dissembly of polyribosomes, defective methylation and acceptor function of transfer RNA, and inhibition of the production of protein. Its incorporation into DNA leads to a covalent binding with DNA methyltransferases, which prevents DNA synthesis and subsequent cytotoxicity. Being a ribonucleoside, it has been shown effective against HIV and HTLV.
Disclaimer:
Information on this page is provided for general information purposes. You should not make a clinical treatment decision based on information contained in this page without consulting other references including the package insert of the drug, textbooks and where relevant, expert opinion. We cannot be held responsible for any errors you make in administering drugs mentioned on this page, nor for use of any erroneous information contained on this page.